Updated on October 29th, 2024 by Bob Ciura
Charlie Munger died on November 28th, 2023 at the age of 99. He was Warren Buffett’s business partner and vice-chairman of Berkshire Hathaway (BRK.B), one of the largest and most well regarded U.S. companies.
Due to the leadership of Munger and Buffett, Berkshire’s historical investing track record is second-to-none. There is plenty for investors to learn from studying Berkshire’s stock holdings.
You can download Berkshire Hathaway’s stock portfolio below:
Warren Buffett tends to get most of the attention when it comes to the discussion of Berkshire’s remarkable performance over the past several decades. But Munger played a vital role in Berkshire’s growth.
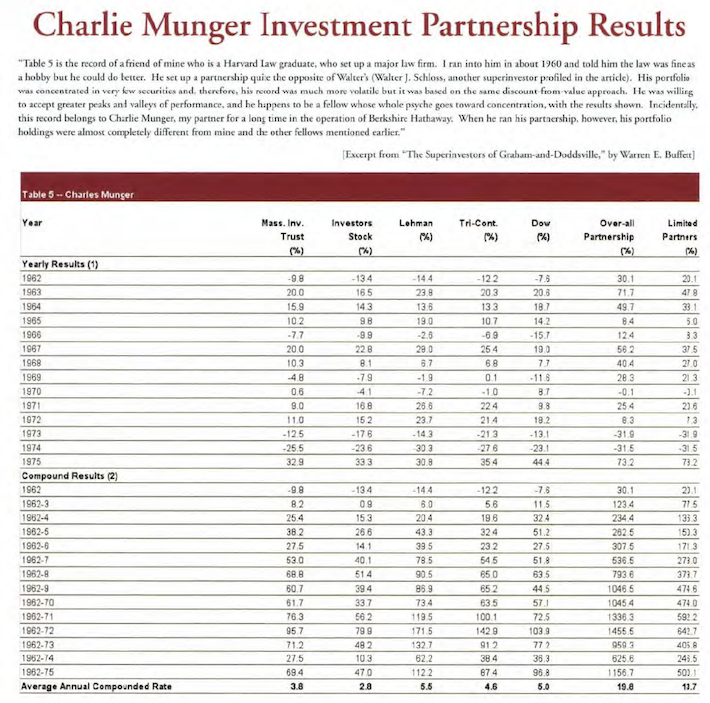
Munger actually managed his own investment partnership before teaming up with Buffett at Berkshire Hathaway. Munger’s own partnership averaged returns of 19.8% a year from 1962 to 1975 versus just 5% a year for the Dow Jones Industrial Average over the same period.
This article provides an overview of Munger’s most interesting quotes. Investors can learn from his actionable insights and incorporate them in both business and life.
Table of Contents
You can jump to a particular section of this article with the links below:
- Charlie Munger’s Life & Investment Partnership Results
- Munger, Buffett, & Investing
- Mental Models
- On Learning
- On Psychology
- On When To Buy
- On Diversification
- On When To Sell
- On Risk
- On Accounting
- On Investing Fees
- On Living a Virtuous and Fulfilling Life
- Charlie Munger on Warren Buffett
- Quotes from Berkshire’s 2022 Annual Report
- What Other People Have To Say About Charlie Munger
- Final Thoughts
Charlie Munger’s Life & Investment Partnership Results
Charlie Munger had a long life, living until almost 100. His life could be best summarized with the following from the acclaimed book Poor Charlie’s Almanack:
Source: Poor Charlie’s Almanack
As mentioned, he previously ran his own investing partnership. Looking at his remarkable track record can help us to understand why we might be able to learn from this fantastic investor. The track record of the Charlie Munger investing partnership is shown below.
Source: Poor Charlie’s Almanack
Munger’s limited partners realized 19.8% annualized returns during the lifetime of the partnership (before fees), comparing very favorably to the 5.0% return realized by the Dow Jones Industrial Average in the same time period. Clearly, we have a lot to learn from this great investor.
Munger, Buffett, & Investing
Charlie Munger heavily influenced Warren Buffett’s investment style. Munger believed in holding a hyper-concentrated portfolio of extremely high-quality businesses. Munger eschewed diversification – he was comfortable holding as few as 3 securities at a time.
Munger’s philosophy of buying and holding high-quality businesses for the long-run clearly rubbed off on Buffett. Before Munger, Buffett was much more of a traditional value investor. After Munger, Buffett focused on high-quality businesses trading at fair or better prices.
One of the main differentiators between Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger was Munger’s insistence on thinking through “mental models”, which we explain below.
Mental Models
Charlie Munger’s interests went far beyond investing. He was a generalist with broad knowledge across multiple fields. Munger was perhaps best known for his ‘mental models’ approach to solving problems.
Warren Buffett says Munger had “the best 30 second mind in the world. He goes from A to Z in one move. He sees the essence of everything before you even finish the sentence“.
Munger advised you understand the ‘big ideas’ from a wide range of subjects – from philosophy, science, physics, investing, and so on. This ‘latticework’ of mental models will help you come to correct conclusions by viewing the problem from multiple vantage points.
Charlie Munger’s mental models approach to life gave him a unique perspective. The remainder of this article is dedicated to presenting and analyzing quotes from Charlie Munger as they apply to business, investing, and living a fulfilling life.
On Learning
Munger was perhaps best-known as a devoted life-long learner in a wide number of disciplines. Munger thought that universities should include a class called “Remedial Worldly Wisdom” that taught all the concepts that students should have learned prior to enrolling.
Because of Munger’s reputation as a passionate learner, it’s useful to understand his definition of wisdom:
“What is elementary, worldly wisdom? Well, the first rule is that you can’t really know anything if you just remember isolated facts and try and bang ’em back. If the facts don’t hang together on a latticework of theory, you don’t have them in a usable form.
You’ve got to have models in your head. And you’ve got to array your experience – both vicarious and direct – on this latticework of models. You may have noticed students who just try to remember and pound back what is remembered. Well, they fail in school and fail in life. You’ve got to hang experience on a latticework of models in your head.”
As this quote suggests, Munger relied heavily on mental models in his pursuit to understand the world around him. Munger thought it was important to understand the “big ideas” from the “big disciplines,” and generalize from there:
“You must know the big ideas in the big disciplines and use them routinely – all of them, not just a few. Most people are trained in one model – economics, for example – and try to solve all problems in one way. You know the old saying: To the man with a hammer, the world looks like a nail. This is a dumb way of handling problems.”
If mental models are so important, this begs the question – how does one learn them?
Munger believed that the best way to learn is by mastering the best that other people have figured out:
“I believe in the discipline of mastering the best that other people have ever figured out. I don’t believe in just sitting down and trying to dream it all up yourself. Nobody’s that smart…”
Munger also believed it is imperative to learn from others’ past mistakes:
“We recognized early on that very smart people do very dumb things, and we wanted to know why and who, so that we could avoid them.”
To learn from others, Munger’s favorite medium was reading.
Source: Poor Charlie’s Almanack
Reading and understanding the great ideas in philosophy, economics, science, and other disciplines slowly opens your mind to different possibilities in a way that staying in one narrow field alone will never be able to accomplish.
It’s also important to have the inborn temperament to always learn more. Munger described how some people have an internal disposition for learning in the following passage:
“How do some people get wiser than other people? Partly it is inborn temperament. Some people do not have a good temperament for investing. They’re too fretful; they worry too much. But if you’ve got a good temperament, which basically means being very patient, yet combine that with a vast aggression when you know enough to do something, then you just gradually learn the game, partly by doing, partly by studying. Obviously, the more hard lessons you can learn vicariously, instead of from your own terrible experiences, the better off you will be. I don’t know anyone who did it with great rapidity. Warren Buffett has become one hell of a lot better investor since the day I met him, and so have I. If we had been frozen at any given stage, with the knowledge hand we had, the record would have been much worse than it is. so the game is to keep learning, and I don’t think people are going to keep learning who don’t like the learning process.”
When it came to learning, Munger particularly emphasized the hard sciences. He studied mathematics as an undergraduate student (though he never completed that degree), and maintained his bias toward quantitative subjects for the rest of his life.
“If you don’t get this elementary, but mildly unnatural, mathematics of elementary probability into your repertoire, then you go through a long life like a one–legged man in an ass–kicking contest. You’re giving a huge advantage to everybody else.”
Munger believed that permutations and combinations (which come from the field of math known as combinatorics that helps answer questions like “how many ways are there to order a group of numbers?”) were especially useful.
“And the great useful model, after compound interest, is the elementary math of permutations and combinations.”
Munger was clearly an unorthodox learner. Given this knowledge, it is unsurprising that he thinks the current post-secondary education system is broken:
“There’s a lot wrong [with American universities]. I’d remove three-fourths of the faculty – everything but the hard sciences. But nobody’s going to do that, so we’ll have to live with the defects. It’s amazing how wrongheaded [the teaching is]. There is fatal disconnectedness. You have these squirrelly people in each department who don’t see the big picture.”
This poor teaching is especially present in the field of investing, as the following quotes illustrate:
“Beta and modern portfolio theory and the like – none of it makes any sense to me. We’re trying to buy businesses with sustainable competitive advantages at a low, or even a fair, price.”
“How can professors spread this [nonsense that a stock’s volatility is a measure of risk]? I’ve been waiting for this craziness to end for decades. It’s been dented, but it’s still out there.”
“Warren once said to me, “I’m probably misjudging academia generally [in thinking so poorly of it] because the people that interact with me have bonkers theories.”
To Munger, learning was one of the best ways to improve in business, investing, and in life.
“Those who keep learning, will keep rising in life.”
And, helping others to learn can be just as valuable:
“The best thing a human being can do is to help another human being know more.”
Munger’s ability and willingness to learn were among the reasons he became such a great investor. Another reason was his patient temperament. Munger’s thoughts on the importance of psychology in life and investing are discussed below.
On Psychology
Charlie Munger loved psychology. In a speech called The Psychology of Human Misjudgment that Munger delivered to Caltech students in 1995, he outlined his perspective on the 25 cognitive biases that have the greatest ability to impair human decision-making.
The 25 biases are:
- Reward and Punishment Superresponse Tendency
- Liking/Loving Tendency
- Disliking/Hating Tendency
- Doubt-Avoidance Tendency
- Inconsistency-Avoidance Tendency
- Curiosity Tendency
- Kantian Fairness Tendency
- Envy/Jealousy Tendency
- Reciprocation Tendency
- Influence-from-Mere-Association Tendency
- Simple, Pain-Avoiding Psychology Denial
- Excessive Self-Regard Tendency
- Overoptimism Tendency
- Deprival-Superreaction Tendency
- Social-Proof Tendency
- Contrast-Misreaction Tendency
- Stress-Influence Tendency
- Availability-Misweighting Tendency
- Use-It-or-Lose-It Tendency
- Drug-Misinfluence Tendency
- Senescence-Misinfluence Tendency
- Authority-Misinfluence Tendency
- Twaddle Tendency
- Reason-Respecting Tendency
- Lollapalooza Tendency – The Tendency to Get Extreme Consequences From Confluences of Psychology Tendencies Acting in Favor of a Particular Outcome
Each of these ideas is outside the scope of this article. If you’re interested in learning more about them, we recommend reading Poor Charlie’s Almanack. With this said, you will likely notice Munger’s emphasis on psychology throughout the rest of this article, as we explore how more of his quotes apply to other areas of business and life.
On When To Buy
As we saw earlier, Munger ran his own investment partnership that beat the market over a meaningful period of time. He also has a strong impact on Berkshire Hathaway’s investment decisions to this day. Accordingly, his thoughts on when to buy stocks are worth discussing.
Munger’s investment strategy was very boring. Keeping a cool head and investing in high-quality businesses with long histories of rewarding shareholders may not be as exciting, but it will generate solid returns over time with less risk than investing in ‘the next big thing’. When the crowd moves on, large losses often follow large gains. Munger sought opportunity that is attractive when adjusted for risk. In other words, he looked for mispriced gambles.
“You’re looking for a mispriced gamble. That’s what investing is. And you have to know enough to know whether the gamble is mispriced. That’s value investing.”
Usually, this entailed buying businesses below their intrinsic value. Buying businesses below their fair value requires you have an idea of what fair value is. When the crowd becomes overly pessimistic they focus on negative possibilities and discount positive possibilities. Having a better estimate of the real probabilities gives an investor a sizeable edge that can be exploited.
Unfortunately, severely ‘mispriced gambles’ don’t come along often. Munger recommended waiting for the best opportunities to come around. When they do, move quickly and decisively.
“If you took our top fifteen decisions out, we’d have a pretty average record. It wasn’t hyperactivity, but a hell of a lot of patience. You stuck to your principles and when opportunities came along, you pounced on them with vigor.”
The opportunities Munger looked for are great businesses trading at a discount to their fair value.
“A great business at a fair price is superior to a fair business at a great price.”
So what defines a great business? Munger thought that a key characteristic of a good business was one that required minimal reinvestment. Said differently, Munger appreciated the ability to withdraw cash from a strong performing business.
On the surface, it might seem like this is always the case. The following passage explains why this isn’t true in practice:
“There are two kinds of businesses: The first earns twelve percent, and you can take the profits out at the end of the year. The second earns twelve percent, but all the excess cash must be reinvested – there’s never any cash. It reminds me of the guy who sells construction equipment – he looks at his used machines, taken in as customers bought new ones, and says “There’s all of my profit, rusting in the yard.” We hate that kind of business.”
Munger also favored business models that were easy to understand, and more importantly, easy to manage. Investors cannot control who gets appointed to lead the companies they invest in, so it is important to focus on businesses that don’t require a genius to be run effectively.
“Invest in a business any fool can run, because someday a fool will. If it won’t stand a little mismanagement, it’s not much of a business. We’re not looking for mismanagement, even if we can withstand it.”
Once an investor finds a great business, it’s important to be willing to give it time. To Charlie Munger, patience was a virtue:
“The big money is not in the buying or the selling, but in the waiting.”
Munger used the economic concept of opportunity cost to filter through investment opportunities.
“Opportunity cost is a huge filter in life. If you’ve got two suitors who are really eager to have you and one is way the hell better than the other, you do not have to spend much time with the other. And that’s the way we filter out buying opportunities.”
Indeed, it’s hard to overstate the importance of opportunity cost in Munger’s investment philosophy. The Berkshire investment managers eschew academic investment analysis techniques like weighted average cost of capital (WACC), instead preferring the far-simpler opportunity cost. The following exchange between Warren Buffett and Charlie Munger at a Berkshire Hathaway annual meeting illustrated this:
Buffett: Charlie and I don’t know our cost of capital. It’s taught at business schools, but we’re skeptical. We just look to do the most intelligent thing we can with the capital that we have. We measured anything against our alternatives. I’ve never seen a cost-of-capital calculation that made sense to me. Have you, Charlie?
Munger: Never. If you take the best text in economics by Mankiw, he says intelligent people make decisions based on opportunity costs – in other words, it’s your alternatives that matter. That’s how we make all of our decisions. The rest of the world has gone off on some kick – there’s even a cost of equity capital. A perfectly amazing mental malfunction.
Munger also believed that a compelling competitive advantage was one reason to be interested in a stock. What stands out about Munger’s analysis of competitive advantages is how he related them to disciplines outside of the world of investing. As an example, Munger related geometry to scale-based competitive advantages (often called economies of scale) in the following passage.
“Let’s go through a list – albeit an incomplete one – of possible advantages of scale. Some come from simple geometry. If you’re building a great circular tank, obviously, as you build it bigger, the amount of steel you use in the surface goes up with the square and the cubic volume goes up with the cube. So as you increase the dimensions, you can hold a lot more volume per unit area of steel.
And there are all kinds of things like that where the simple geometry- the simple reality- gives you an advantage of scale.”
It’s also worth mentioning that Munger (and, by extension, Berkshire Hathaway) did not make investment decisions based on macroeconomics. In response to the question “What macro statistics do you regularly monitor or find useful in your attempt to understand the broader economic landscape?” Munger said:
“None. I find by staying abreast of our Berkshire subsidiaries and by regularly reading business newspapers and magazines, I am exposed to an enormous amount of material at the micro level. I find that what I see going on there pretty much informs me of what’s happening at the macro level.”
We’ve seen that Munger liked to buy great businesses with sustainable competitive advantages when they trade at fair or better prices. The next section discusses his thoughts on portfolio diversification.
On Diversification
As mentioned earlier in this article, Charlie Munger ignored diversification in the traditional sense. Munger was comfortable owning as few as three stocks.
Munger’s concentrated approach to investing flows from the idea of using your capital on your best ideas. The cost of diversifying is forgoing putting more capital to work in your best idea. Viewed in this manner, a concentrated portfolio is logical – if you have a high conviction your forecasts are accurate.
“The idea of excessive diversification is madness.”
Munger believed that taking money you could invest in your best idea and putting it into your 100th best idea doesn’t make sense. The greater degree of certainty you have in your investing skill, the fewer securities you need to own in your portfolio.
Moreover, less diversification means a greater focus on the few especially important opportunities that come around in someone’s lifetime.
“Our experience tends to confirm a long-held notion that being prepared, on a few occasions in a lifetime, to act promptly in scale, in doing some simple and logical thing, will often dramatically improve the financial results of that lifetime.
A few major opportunities, clearly recognized as such, will usually come to one who continuously searches and waits, with a curious mind that loves diagnosis involving multiple variables.
And then all that is required is a willingness to bet heavily when the odds are extremely favorable, using resources available as a result of prudence and patience in the past. “
Munger’s behavior with respect to diversification was highly unusual. His decisions on when to sell stocks are similarly atypical and discussed in the next section of this article.
On When To Sell
Charlie Munger was a notoriously long-term investor. This was because there are a number of significant benefits that come from owning great businesses for long periods of time. Munger’s thoughts on long-term investing can be seen below.
“We’re partial to putting out large amounts of money where we won’t have to make another decision. If you buy something because it’s undervalued, then you have to think about selling it when it approaches your calculation of its intrinsic value. That’s hard. But if you buy a few great companies, then you can sit on your ass. That’s a good thing.”
Munger held for the long-term partially because his conservative, low-risk investment strategy worked best when applied for very long periods of time. His investments were slow-and-steady decisions that, in aggregate, outperformed competitors with more irrational risk tolerance. This naturally brings the tortoise-and-the-hare analogy to mind:
“It is occasionally possible for a tortoise, content to assimilate proven insights of his best predecessors, to outrun hares that seek originality or don’t wish to be left out of some crowd folly that ignores the best work of the past. This happens as the tortoise stumbles on some particularly effective way to apply the best previous work, or simply avoids standard calamities. We try more to profit from always remembering the obvious than from grasping the esoteric. It is remarkable how much long-term advantage people like us have gotten by trying to be consistently not stupid, instead of trying to be very intelligent.”
As implied above, Munger’s risk tolerance was very conservative. The next section discusses Munger’s risk tolerance in detail.
On Risk
Munger had little risk tolerance and was a very conservative investor. With that said, he recognized that there is some risk inherent in any investment, and anyone who says this isn’t true should be avoided.
“When any guy offers you a chance to earn lots of money without risk, don’t listen to the rest of his sentence. Follow this, and you’ll save yourself a lot of misery.”
Munger realized that there are far too many people looking to take advantage of less informed investors. There are also many people who mean well but don’t understand the risk they are taking. If something seems too good to be true, it probably is.
This certainly holds when it comes to derivatives and other complicated financial instruments. Munger said the following on derivatives:
“It’s easy to see [the dangers] when you talk about [what happened with] the energy derivatives – they went kerflooey. When [the companies] reached for the assets that were on their books, the money wasn’t there. When it comes to financial assets, we haven’t had any such denouement, and the accounting hasn’t changed, so the denouement is ahead of us.”
Munger’s aversion to using derivatives came from a lack of knowledge about their intrinsic value. While the Black-Scholes model is often used to value stock options for accounting purposes, this model is flawed. Munger explained this below:
“Black-Scholes is a know-nothing system. If you know nothing about value – only price – then Black-Scholes is a pretty good guess at what a ninety-day option might be worth. But the minute you get into longer periods of time, it’s crazy to get into Black-Scholes.”
Separately, Munger said:
“For example, at Costco we issued stock options with strike prices of $30 and $60, and Black-Scholes valued the $60 ones higher. This is insane.”
Note: Charlie Munger is a long-time member of Costco’s Board of Directors.
Munger’s risk-aversion was a key component of his investment philosophy, and translated to his opinion on current accounting schemes – discussed below.
On Accounting
Munger found the creative accounting employed by many corporate managers to be highly distasteful. An explanation of this (in the context of the Enron accounting fraud) is shown below.
“Creative Accounting is an absolute curse to a civilization. One could argue that double-entry bookkeeping was one of history’s great advances. Using accounting for fraud and folly is a disgrace. In a democracy, it often takes a scandal to trigger reform. Enron was the most obvious example of a business culture gone wrong in a long, long time.”
Munger especially disliked EBITDA as a proxy for corporate earnings:
“I think that, every time you see the word EBITDA, you should substitute the words “bullsh*t earnings.”
If there is anything that Munger disliked more than creative accounting, it’s high investing fees. We discuss Munger’s stance on investing fees below.
On Investing Fees
In Poor Charlie’s Almanack, there are plenty of passages that describe Munger’s stance on high investing fees. In particular, Munger disliked the investment management business because he believed that it doesn’t add anything to society in aggregate. He also believed that the probability that a client is being harmed by their investment manager is commensurate with the fees they’re paying.
“Everywhere there is a large commission, there is a high probability of a rip-off.”
Outperforming the market is very difficult. When investors pay large fees, it becomes virtually impossible. The lower your investing costs, the more money you can put to work in the stock market for yourself. ‘Just’ 1% or 2% a year adds up to a tremendous amount of lost money over the course of an investing lifetime.
Munger believed that the best way to minimize investment fees was to invest for the long-term. Munger succinctly summarized the cost benefits of long-term investing:
“You’re paying less to brokers, you’re listening to less nonsense, and if it works, the tax system gives you an extra, one, two, or three percentage points per annum.”
Thus, Munger’s dislike of investing fees and his long-term investing style are connected.
Thus far, we have focused on discussing Munger’s wisdom as it relates to business and investing. The remainder of this article will focus on Munger’s wisdom as it relates to personal life.
On Living A Virtuous and Fulfilling Life
Charlie Munger believed the key to personal and professional success is simple. Devote your life to something you are passionate about, and good at.
“You’ll do better if you have passion for something in which you have aptitude. If Warren had gone into ballet, no one would have heard of him.”
Munger and his business partner Warren Buffett stand out among successful businessmen because of their character, honesty, and integrity. We’ll discuss the character-related principles of Charlie Munger’s life step-by-step in this section.
Munger believed that avoiding envy is an integral component of living a happy and prosperous life. When it came to building wealth, he warned against the jealousy that may come from other people outperforming you.
“Someone will always be getting richer faster than you. This is not a tragedy.”
There will always be a subsector of the economy that is ‘on fire’. The investors who happen to be in this subsector will show phenomenal results – for a time.
A great business at a fair price compounds investor wealth year after year. A fair business at a great price only offers the potential to compound investor returns when it reaches fair value – then it must be sold. A great business potentially never needs to be sold.
Another component of Munger’s personality was a strong belief that people should be reliable. In other words, people should do what they say they’re going to do. The following quote, written by Munger in Poor Charlie’s Almanack, illustrates this point nicely:
“Indeed, I have often made myself unpopular on elite college campuses pushing this reliability theme. What I say is that McDonald’s is one of our most admirable institutions. Then, as signs of shock come to surrounding faces, I explain that McDonald’s, providing first jobs to millions of teenagers, many troubled, over the years, has successfully taught most of them the one lesson they most need: to show up reliably for responsible work. Then I usually go on to say that if the elite campuses were as successful as McDonald’s in teaching sensibly, we would have a better world.”
To Charlie Munger, being unreliable was not just an undesirable quality, but it could also hold a person back in their life:
“What do you want to avoid? Such an easy answer: sloth and unreliability. If you’re unreliable, it doesn’t matter what your virtues are. You’re going to crater immediately. Doing what you have faithfully engaged to do should be an automatic part of your conduct. You want to avoid sloth and unreliability.”
Munger also believed that honesty is one of the most important characteristics an individual can have.
“I think track records are very important. If you start early trying to have a perfect one in some simple thing like honesty, you’re well on you way to success in this world.”
This extends to his behavior as a steward of shareholder capital at Berkshire Hathaway. Munger would rather honestly underperform than report dishonest financial results that please his investors.
“Today, it seems to be regarded as the duty of CEOs to make the stock go up. This leads to all sorts of foolish behavior. We want to tell it like it is.”
The job of a CEO is to maximize long-term value for shareholders. Often, long-term value maximization comes at the expense of short-term profits.
CEOs who seek to boost the stock price at all costs will repurchase shares at the worst possible times and pursue short-term profits above all else, destroying shareholder value in the process. It also harms the manager’s reputation.
“Remember that reputation and integrity are your most valuable assets – and can be lost in a heartbeat.”
In the short-run, people and businesses can get richer faster by being dishonest. In the long run, honesty and integrity build a reputation that is worth more than the quick gains that come from trickery. Being honest and acting with integrity makes it easy to sleep at night.
“Our ideas are so simple that people keep asking us for mysteries when all we have are the most elementary ideas.”
In addition to honesty and integrity, Munger advocated humility as well. In Munger’s view, excessive ego can get investors and business leaders in trouble.
“If you think your IQ is 160 but it’s 150, you’re a disaster. It’s much better to have a 130 IQ and think it’s 120.”
Like other great investors, Charlie Munger advocated simplicity. Keeping things simple greatly reduces errors. The more complicated an idea or investment thesis, the more likely it is to be wrong. This is because there are simply too many moving parts and too many estimates that are all prone to error.
Munger and Buffett long steered away from businesses that were too complicated to understand:
“We have three baskets for investing: yes, no, and too tough to understand.”
Lastly, Munger also had some valuable career advice:
“I have three basic rules. Meeting all three is nearly impossible, but you should try anyway:
- Don’t sell anything you wouldn’t buy yourself.
- Don’t work for anyone you don’t respect and admire.
- Work only with people you enjoy.
I have been incredibly fortunate in my life: with Warren I had all three.”
Charlie Munger on Warren Buffett
Munger is often cited as having had a profound impact on Warren Buffett’s investment strategy. With that said, Munger often stated that he receives too much credit for this.
“I think those authors give me more credit than I deserve. It is true that Warren had a touch of brain block from working under Ben Graham and making a ton of money – it’s hard to switch from something that’s worked so well. But if Charlie Munger had never lived, the Buffett record will still be pretty much what it is.”
“I think there’s some mythology in the idea that I’ve been this great enlightener of Warren. He hasn’t needed much enlightenment. But we know more now than five years ago.”
Munger also believed that Buffett’s exceptional competency means that his successor likely will not be as intelligent. To be fair, Buffett’s successor will have large shoes to fill.
“I think the top guy won’t be as smart as Warren. But it’s silly to complain: “What kind of world is this that gives me Warren Buffett for forty years, and then some bastard comes along who’s worse?”
Quotes from Berkshire Hathaway’s 2022 Annual Report
Berkshire’s annual reports are typically written by Warren Buffett. The 2022 annual report had several insightful quotes from Charlie Munger.
“You have to keep learning if you want to become a great investor. When the world changes, you must change.”
The above quote highlights the importance of lifelong learning in investing. You must keep learning and improving as the world changes.
“There is no such thing as a 100% sure thing when investing. Thus, the use of leverage is dangerous. A string of wonderful numbers times zero will always equal zero. Don’t count on getting rich twice.”
Leverage can lead total capital impairment. Losing it all means you start at nothing; well nothing but a worse reputation. Being conservative with investing may mean slower wealth accumulation in the short run, but it also typically means a higher probability of compounding wealth over the long run.
“Warren and I don’t focus on the froth of the market. We seek out good long-term investments and stubbornly hold them for a long time.”
&
“The world is full of foolish gamblers, and they will not do as well as the patient investor.”
Munger and Buffett’s investing style was to seek out high quality businesses and hold them for the long run. They avoided ‘market froth’ and are not ‘foolish investors’. Instead they were ‘patient investors’ who ‘seek out good long-term investments’.
What Other People Have To Say About Charlie Munger
Charlie Munger is adored by many other members of the professional investment community. The following set of quotes illustrates the excellent reputation that Munger has crafted over the decades while also providing additional insight into his personality and investment philosophy.
“I was in New York City with Charlie to attend a Salomon Brothers board meeting. We had come out of the building and were standing on the sidewalk, discussing what had transpired at the meeting. At least, that‘s what I thought we were doing, for suddenly I realized that I had been talking to myself for some time. I looked around for Charlie, only to see him climbing into the back of a taxicab, headed off to the airport. No goodbye, no nothing.
People think it‘s Charlie’s eyes that cause him to miss seeing things (Charlie lost his vision in one eye many years ago due to complications from cataract surgery). BUT IT’S NOT HIS EYES, IT’S HIS HEAD! I once sat through three sets of traffic lights, and plenty of honking behind us, as Charlie discussed some complex problem at an intersection.”
“I would say everything about Charlie is unusual. I’ve been looking for the usual now for forty years, and I have yet to find it. Charlie marches to his own music, and it’s music like virtually no one else is listening to. So, I would say that to try and typecast Charlie in terms of any other human that I can think of, no one would fit. He’s got his own mold.” – Warren Buffett, CEO and Chairman of Berkshire Hathaway
I can attest that Chalie has a combination of characteristics that I have never seen in any other single individual. He has an extraordinary and deep intelligence across a broad range of interests, and he never seems to forget anything, no matter how arcane or trivial. On top of these attributes is his absolute commitment to honesty, ethics, and integrity – Charlie never “grabs” for himself and can be trusted without reservation. If that’s not enough, he has a temperament toward investing that can only be described as ideal: unyielding patience, discipline, and self-control – Charlie just doesn’t crack or compromise on his principles, no matter how stressful the situation.” – Louis A. Simpson, President and CEO, Capital Operations, GEICO Corporation
When Charlie is in deep thought, he often loses track of a lot of what’s going on around him, including social niceties. I remember that when we were negotiating with CenFed to have them take over our savings and loan business, Charlie and I went over to their offices to meet with their CEO, Ted Lowrey. We had a perfectly wonderful meeting – Charlie can put on the charm if he puts his mind to it – and we were winding things up very satisfactorily.
“Ted walked us to the elevator. Just as we got there, the elevator door opened, and Charlie walked directly inside. He never said goodbye, never shook hands, nothing. Tad and I were left standing there, smiling and speechless.” – Bob Bird, President, Wesco Financial. Also Munger’s friend and business asscoiate since 1969.
“When it comes to being curious and focused, when Charlie gets interested in something, he REALLY gets interested in it. I remember three talks he prepared and presented to our law firm on some of what he referred to as ‘the eminent dead‘ he had encountered through his extensive reading: Isaac Newton, Albert Einstein, and Simon Marks. In particular, I remember the central message of the talk on Simon Marks (of retailer Marks and Spencer): ‘Find out what you’re best at and keep pounding away at it.’ This, of course, has always been Charlie’s basic approach to life.” – Dick Esbenshade, Munger’s friend and business associate since 1956.
“For years, I would see Charlie at our Southern California beach house. I remember having ‘conversations’ that were essentially one-sided, feeling like I should have a dictionary at my side to look up all the words I didn’t understand. I remember not saying much, being scared to ask a question and appearing stupid. He’s so darned smart, like my father, in the stratosphere.” – Howard Buffet, Warren Buffett’s son.
“Charlie had a desire to understand exactly what makes things happen. He wants to get to the bottom of everything, whether it’s something of serious interest to him or not. Anything that comes to his attention, he wants to know more about it and understand it and figure out what makes it tick.” – Roy Tolles, co-founder of Munger’s original law firm.
“He knows how to take all of his brains and all of his energy and all of his thought and focus exactly on a single problem, to the exclusion of anything else. People will come into the room and pat him on the back or offer him another cup of coffee or something, and he won’t even acknowledge their presence because he is using one hundred percent of his huge intellect.” – Glen Mitchel, Munger’s friend since 1957.
Final Thoughts
Charlie Munger died on November 28th at age 99. Charlie Munger’s mental models approach to investing produced phenomenal success for Munger himself and for Berkshire Hathaway. His unique perspective was a combination of the wisdom of several fields. At its core, Charlie Munger’s approach was similar to Warren Buffett’s – invest in high-quality businesses that generate above-average returns.
Businesses that generate above-average returns must have a competitive advantage that prohibits competitors from undercutting the company. Patents, strong brand names, and economies of scale can all result in above average returns.
The Dividend Aristocrats List is an excellent place to look for high-quality businesses. To become a Dividend Aristocrat, a business must pay increasing dividends for 25 or more consecutive years in a row.
In some ways, this is unsurprising; the Dividend Aristocrats have many characteristics that would make Munger smile.
Other Dividend Lists
The following lists contain many more quality dividend stocks:
- The High Yield Dividend Aristocrats List is comprised of the 20 Dividend Aristocrats with the highest current yields.
- The Dividend Achievers List is comprised of ~400 stocks with 10+ years of consecutive dividend increases.
- The Dividend Kings List is even more exclusive than the Dividend Aristocrats. It is comprised of 54 stocks with 50+ years of consecutive dividend increases.
- The High Yield Dividend Kings List is comprised of the 20 Dividend Kings with the highest current yields.
- The Blue Chip Stocks List: stocks that qualify as Dividend Achievers, Dividend Aristocrats, and/or Dividend Kings
- The High Dividend Stocks List: stocks that appeal to investors interested in the highest yields of 5% or more.
- The Monthly Dividend Stocks List: stocks that pay dividends every month, for 12 dividend payments per year.
- The Dividend Champions List: stocks that have increased their dividends for 25+ consecutive years.
Note: Not all Dividend Champions are Dividend Aristocrats because Dividend Aristocrats have additional requirements like being in The S&P 500. - The Dividend Contenders List: 10-24 consecutive years of dividend increases.
- The Dividend Challengers List: 5-9 consecutive years of dividend increases.